The best way to protect yourself, your users and your business against ransomware is by setting up a proactive defence. The ransomware statistics paint a frightening picture for anyone in charge of IT: In Q3 2016 alone, 18 million new malware samples were captured. Source: Panda Labs What that means is that the criminals…
Petya Ransomware Hits South Africa
Just as IT managers the world over were exhaling after the Wannacry ransomware outbreak, the world has been hit with a new attack in the form of Petya.
Originally circulated in 2016, this latest malware is an offshoot of Petya but with stronger encryption, the new version has been dubbed “NotPetya” or “GoldenEye,” with some still referring to it as “Petya.”
This viscious strain is targeting countries including the United States, South Africa and the United Kingdom. Petya has already infected 2000 targets including global corporations like Maersk, Merck, and organisations in the Ukraine where it seems to have originated.
Get the Cibecs Ransomware Protection Toolkit
The attack appears to have been originally deployed through an automatic software update feature built into an accounting program. Like WannaCry, Petya uses EternalBlue, a hacking weapon developed by the NSA and leaked online.
While both strains have used the same weapon, it looks like Petya is harder to stop. According to Bogdan Botezatu, a researcher at Bitdefender, “The quality of the code improves from iteration to iteration—this GoldenEye ransomware is pretty solid.”
Educate your Users on how to Protect themselves from Malware
Wannacry contained a kill switch in the form of a badly coded feature meant to help the program avoid analysis, unfortunately, the latest version of Petya does not seem to have something like this. What makes Petya so dangerous is that it does not rely solely on EternalBlue to access systems, it can also deploy other infection options as well. For example, through the software update feature of a Ukrainian program called MeDoc, and most concerning, possibly through Microsoft Word documents laced with malicious macros.
This ransomware also uses the leaked NSA exploit known as EternalRomance for remote access and may be using EsteemAudit, to target computers running Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. Microsoft.
How Prepared are you for a Ransomware Attack? Take the test
Once Petya has access to the network, it steals administrative credentials, to give it control over system management tools like Windows PsExec and Windows Management Instrumentation. With enough administrative privileges, it can instruct all other PCs it has access to, to run the malware.
South Africa’s 702 Radio Station reported this morning that businesses are being attacked when powering up their computers they were shown the screen below.
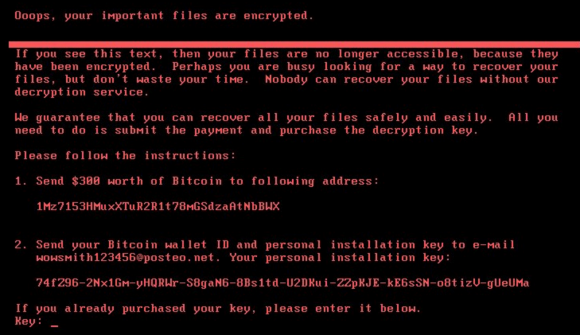
ransomware requires a Bitcoin payment for victims to access the decryption key, however, the email address used to communicate with the attackers has been suspended, meaning that even if a ransom is paid there is no way for victims to get the decryption key and regain access to their data.
“We didn’t even consider paying the ransom” Read how NJR Steel beat ransomware
While Petya is not seeing nearly as many casualties as WannaCry, do not be fooled, the attack seems to be more intentional in its targets and it is at this point extremely difficult to stop. Take steps now to protect your business and data against this ransomware.
Protecting Your Data Against Petya: Six Practical Steps to Take
Unfortunately, the diversity of deployment options means that a single patch can’t provide protection against Petya. However, IT managers and administrators can protect their network from Petya with these steps outlined in our free Checklist PDF. The PDF of Petya Ransomware Protection steps includes:
- How to be able to completely recover users data without paying the Ransom
- What files to stop from running
- What Microsoft protections you should be employing
- How to educate your users and better protect your business computers from Malware.
Get the Free Petya Protection Checklist: 6 Steps to Protect Your Business from Petya
FEATURED POSTS
IT Managers: How to Protect Your Users Against Ransomware
The best way to protect yourself, your users and your business against ransomware is by setting up a proactive defence. The ransomware statistics paint a frightening picture for anyone in charge of IT: In Q3 2016 alone, 18 million new malware samples were captured. Source: Panda Labs What that means is that the criminals…
Cibecs Joins Silicon Valley Top 20
Cibecs Joins Silicon Valley Companies to be Listed on Top 20 Most Promising Storage Solution Providers Cibecs, a leading South African endpoint backup, protection and security solution, has been recognised as one of the 20 Most Promising Storage Solutions by CIO Review. The list, compiled by industry insiders, highlights leading global technology providers that offer effective…
4 Signs You Need a New Endpoint Data Backup Solution
With more workers depending on laptops it is more important than ever to ensure that the work protected and stored on those devices is backed up and protected. Forrester Research says that 45% of corporate executives don’t follow policies for data use and handling. Underlining how at risk almost half of a business’s data actually…